Pain-free patches to revolutionise vax delivery

Crying children scared of the needles used to deliver their vaccinations will soon be a thing of the past, thanks to new technology developed by an Australian University.
Researchers at the University of South Australia have developed a 100% pain-free, dissolvable, antibacterial microneedle patch for delivering vaccinations.
The patches will also reduce the risk of infection and disease through unsafe injection practices by removing needles from the equation. Further, the antibacterial, silver-loaded dissolvable microneedle patches sterilise the injection site to inhibit the growth of bacteria.
The patches will also reduce sharp waste, as they physically dissolve after administration.
Reducing the risk of infection
Lead researcher Professor Krasimir Vasilev said these first-generation microneedles have the potential to transform the safe administration of transdermal vaccinations and drug delivery.
“Injections are one of the most common healthcare procedures used for vaccinations and curative care around the world,” Prof Vasilev said.
“But up to 40% of injections are given with improperly sterilised syringes and needles, placing millions of people at risk of contracting a range of illnesses or diseases.
“Our silver-loaded microneedles have inherently potent antibacterial properties which inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria and reduce the chance of infection.”
The UniSA study, published in Chemical Connections, tested the antibacterial efficacy of silver-loaded microneedles against bacteria associated with common skin infections — Golden staph, Staphylococcus epidermis, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa — and found that the silver-loaded microneedle patches created a 24-hour bacteria-free zone around the patch administration site, a feature unique to the new technology.

Safe, pain-free option
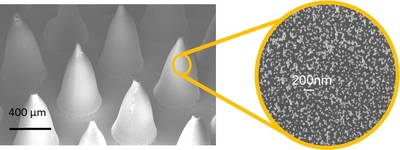
The silver-loaded microneedles comprise an array of 15 x 15 needles each 700 micron in length, which pierce only the top layer of the skin without reaching the underlying nerves, making them 100% painless.
The microneedles are made from a safe, biocompatible and highly water-soluble polymer that completely dissolves within one minute of application, leaving behind no sharp waste.
The World Health Organization said that using the same syringe or needle to give injections to more than one person is driving the spread of deadly infectious diseases worldwide, estimating that this may cause up to 1.7 million people to be infected with hepatitis B, 315,000 with hepatitis C and as many as 33,800 with HIV each year.
Prof Vasilev said the dissolvable feature of the microneedles will significantly improve injection safety.
“Infection from unsafe injection practices occurs all over the world,” Prof Vasilev said, “so technologies that protect people from unnecessary infection are critical.
“The dissolvable feature of our silver-loaded microneedles ensures absolutely no risk of re-use, removing one of the greatest causes of infection.
“And by incorporating the antibacterial silver nanoparticles into the dissolvable microneedles, we’ve created a very promising vehicle for safe vaccine and drug delivery around the world.”
PhD scholarship announced for nursing leadership in digital health
Australian Catholic University has partnered with the Australian College of Nursing, Ausmed and...
Teachers Health Group announces Simone Tregeagle as next CEO
Teachers Health Group, which encompasses Nurses & Midwives Health, has announced that Simone...
Unlawful cosmetic injections land nurse two-year ban
After "unlawfully and inappropriately" injecting a formulation of botulinum toxin into...





![[New Zealand] Transform from Security Awareness to a Security Culture: A Vital Shift for SMB Healthcare — Webinar](https://d1v1e13ebw3o15.cloudfront.net/data/89856/wfmedia_thumb/..jpg)
![[Australia] Transform from Security Awareness to a Security Culture: A Vital Shift for SMB Healthcare — Webinar](https://d1v1e13ebw3o15.cloudfront.net/data/89855/wfmedia_thumb/..jpg)



